MACHINE LEARNING HAS A CARBON ISSUE BUT NOBODY CARES ABOUT IT
by IndustryTrends | Analytics Insights

Machine learning with its advancement has a big issue called Carbon release
There are tremendous computational costs of Machine Learning and AI. Artificial intelligence algorithms, which power some of technology’s most cutting-edge applications, inclusive of producing logical stretches of text or growing visuals from descriptions, can also additionally want large quantities of computational electricity to train. This, in turn, necessitates a vast amount of electricity, prompting many to worry that the carbon footprint of the increasingly famous ultra-large AI structures might render them environmentally unsustainable. Machine learning (ML) is great for augmenting human intelligence, however academic and industry researchers were debating the severity of its carbon footprint. We’re still learning about the significance of machine learning’s outcomes and solving ML issues in the environment, however, there are answers to be had to assist groups to choose the maximum green options for managing and distributing workloads.
Virtual Spaces are More About Interactions Than NFTs
by AR Insider Guest | AR Insider

NFTs continue to face headwinds, dwindling value, and bad actors. But even in their earlier rise, they were largely misunderstood and positioned as a central component of the still-undefined metaverse. Speaking of the m-word, it’s becoming clearer that the real value for consumer brands will be in creating meaningful connections… not necessarily minting and distributing digital goods.
While there is certainly opportunity for brands to sell additional products in the metaverse—fashion retailers like Nike and Gucci are already working on developing pricing strategies for digital goods and services—branding experts believe the greatest long-term gains will be won through marketing approaches that focus on quality interactions and engagement.
“The metaverse is much more than a new, albeit virtual, market for brands to expand into. The opportunity for brands is beyond just selling an additional product — rather, it is about creating a new world of connection, cultural relevance, and clout,” says Anne Olderog, a branding strategist with more than 20 years of experience working with Fortune 500 companies.
The road to quantum-enabled cybersecurity
Dr Francis Gaffney | Open Access Government
Based on the values of quantum mechanics, quantum computers use rapidly emerging technology to effortlessly process complex algorithms. As quantum computers can perform certain types of computations more efficiently than classical computers, they could also pose a significant threat to the current cryptographic cybersecurity systems. This is why there is a need for quantum-enabled cybersecurity.
Quantum computing holds the potential to unlock secrets ranging from one’s personal finances to a nation’s defence strategy. Large-scale quantum computers, if realised, can enable hackers and nation states to break current cryptographic protocols.
In essence, they are capable of threatening the security of commonly used public key cryptosystems and exposing the vulnerabilities that exist within today’s fundamental digital systems that are used to power various internet services, including online financial transactions, e-commerce, and secure communications.
2 Minute Read →
🌙 NASA - Best Photo from Last Week
Hubble Peers at Celestial Cloudscape
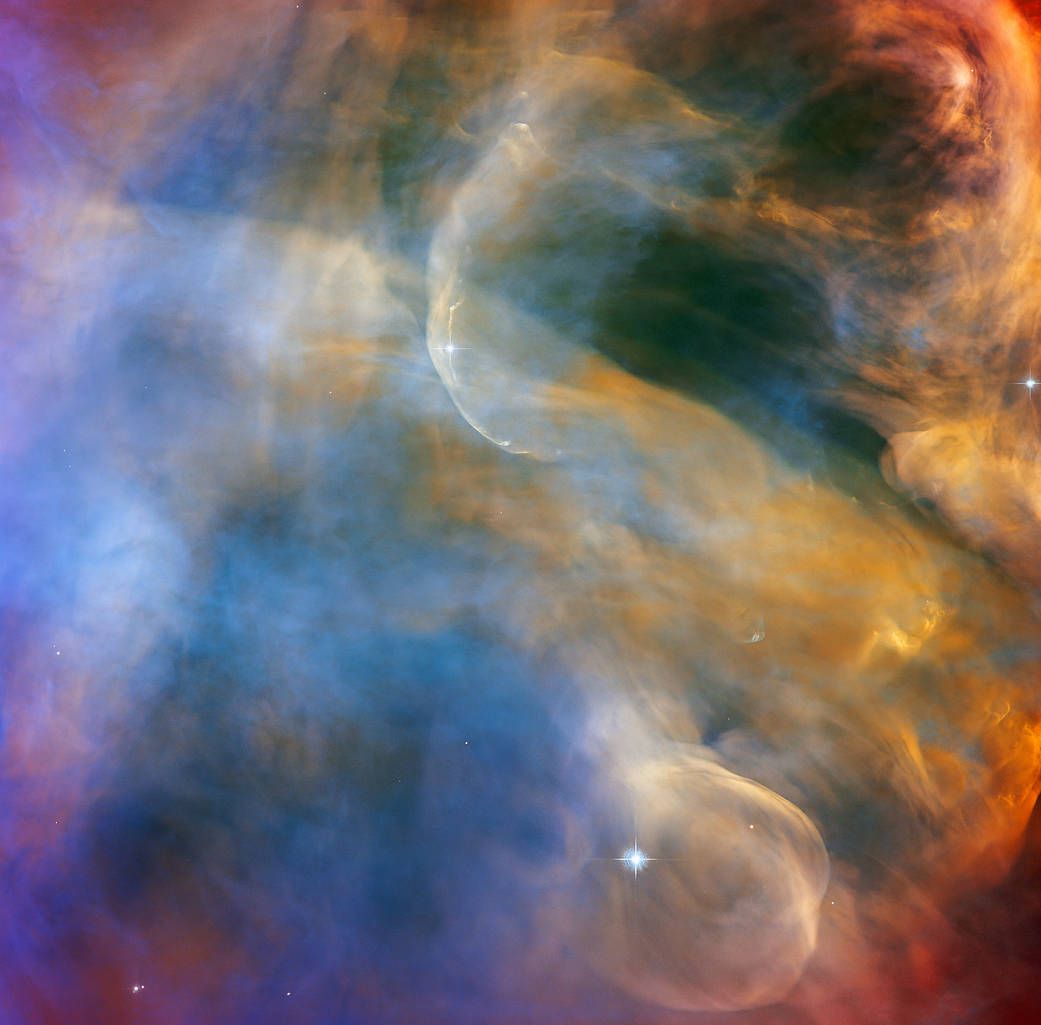

This celestial cloudscape from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope captures the colorful region in the Orion Nebula surrounding the Herbig-Haro object HH 505. Herbig-Haro objects are luminous regions surrounding newborn stars that form when stellar winds or jets of gas spew from these infant stars creating shockwaves that collide with nearby gas and dust at high speeds. In the case of HH 505, these outflows originate from the star IX Ori, which lies on the outskirts of the Orion Nebula around 1,000 light-years from Earth. The outflows themselves are visible as gracefully curving structures at the top and bottom of this image. Their interaction with the large-scale flow of gas and dust from the core of the nebula distorts them into sinuous curves.
Captured with Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) by astronomers studying the properties of outflows and protoplanetary disks, the image reveals bright shockwaves formed by the outflows as well as slower moving currents of stellar material. The Orion Nebula is awash in intense ultraviolet radiation from bright young stars. Hubble’s sensitivity to ultraviolet light allows astronomers to directly observe these high-energy outflows and learn more about their structures.
The Orion Nebula is a dynamic region of dust and gas where thousands of stars are forming. It is the closest region of massive star formation to Earth, making it one of the most scrutinized areas of the night sky and often a target for Hubble. This observation was also part of a spellbinding Hubble mosaic of the Orion Nebula, which combined 520 ACS images in five different colors to create the sharpest view ever taken of the region.
Text credit: European Space Agency (ESA)
Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, J. Bally; Acknowledgment: M. H. Özsaraç
Media Contact:
Claire Andreoli
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD
301-286-1940
Last Updated: Aug 12, 2022
Editor: Andrea Gianopoulos


Disclaimer: None of the content in this newsletter is meant to be financial advice. Please do your own due diligence before taking any action related to content within this article.
Disclaimer: Unbound is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission.






